Joblinomyces was identified in 2020 as a part of a collaborative isolation effort that targeted a wide range of wild, domesticated and zoo-housed herbivores (Hanafy et al, 2020). Joblinomyces was isolated from the feces of a domesticated goat and sheep. Similar to many other genera that have been described to date, Joblinomyces has a monocentric thallus, filamentous rhizoidal system and monoflagellated zoospores.
The genus name, Joblinomyces, was given to honor Prof. Keith N. Joblin for his great contribution to the field of anaerobic fungi. The type species is called J. apicalis, refering to the zoospore release mechanism through the dissolution of a wide apical portion of the sporangial wall. The type strain for the genus is GFH683, which was isolated from the feces of a domesticated goat. To date, no other species have been described for this genus.
Joblinomyces is the first cultured representative of the clade AL5 (Kittelmann et al. 2012), which was first discovered and reported (as NG5) in a previous ITS1-based culture independent survey (Liggenstoffer et al. 2010). Interestingly, sequences affiliated to Joblinomyces were encountered mainly in foregut fermenters, suggesting a preference for foregut rather than hindgut herbivores (Hanafy et al, 2020).
Morphology
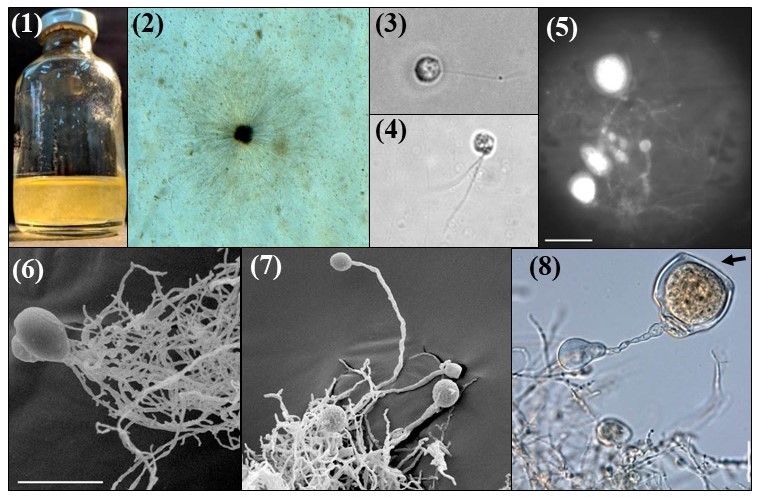
Images are shown above of Joblinomyces apicalis strain GFH683.
In liquid medium, Joblinomyces produces a thin fungal biofilm (Image 1). On solid roll agar medium, it forms colonies with a dark central core surrounded by long and thin radiating rhizoids (Image 2).
Microscopically, Joblinomyces produces mainly monoflagellated zoospores (Image 3), although biflagellated zoospores can also be observed (Image 4). Joblinomyces has monocentric thalli with filamentous anucleate rhizoidal systems (Image 5). Both endogenous (Image 6) and exogenous (Image 7) sporangia are produced.
Zoospores are released through dissolution of the apical portion of sporangial wall, resulting in formation of an empty cup-shaped sporangium (Image 8, arrow).
Sequence Information
No sequenced genome is currently available for Joblinomyces. For the latest update regarding publically available genomes for this genus, please see here.
For the Joblinomyces apicalis strain GFH683 that is pictured above, the LSU sequence is available in the NCBI database (accession number MK910268).
